What happens when we apply our favorite varnish? We explain everything to you in this article.
At Manucurist, we like transparency: we are convinced that cosmetics should not be opaque. It is in this logic that we share our Blacklist of ingredients on our page Philosophy. This allows us to explain to you by which we replace these controversial ingredients and their usefulness in the formula.
But that is not always enough to understand how a varnish works. What is the difference between a Green varnish classic and a Semi-permanent Green Flash? And the Polly Green in all of that ? Here is an article that will allow you to see more clearly!

Classic green varnish, a story of evaporation
Let’s first try to understand what a Green varnish is made up.
🌱Solvents
Solvents constitute the most important part of a varnish: they allow to obtain A homogeneous and liquid formula. In Manucist varnishes, these solvents are butyl acetate and ethyl acetate; they're both bio-sourced (To find out more about bio-sourced, consult our article dedicated).
✨Nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose is what is called a filmogenic agent: he will create a smooth, shiny and dry film quickly.
💅Resins
In classic green varnishes, you can also find resins that allow adhesion of this film on the nail.
💪Plastifiers
Plastifiers, on the other hand, make the film of elastic nitrocellulose, which Improves the outfit : Thus the varnish does not crack and therefore flakes less easily.
🎨Pigments and bentonite
Pigments and pearls (rated CI followed by 5 digits) bring Color and reflections.
Finally, bentonite is used to Fluidify the formula : This is called a thixotropic agent.
When applying a classic varnish, it is in liquid form. Once on the nail, the solvents go evaporate Creating a colorful, solid and shiny film.
The semi-permanent green flash and the light
The semi-permanent formula is very similar to that of classic varnishes. Nevertheless, it is a little more technical since the drying mechanism is different from that of Green varnishes.
Green Flash varnishes contain, in addition, co-polymers: these molecules react with UV emitted by the lamp and bind to each other, forming a polymer network that hardens the gel layer.

Result : After this chemical reaction, a layer of completely solidified varnish is obtained; It is said that the formula catalysis or that it polymerizes. Coupled with the evaporation of solvents, this reaction makes it possible to obtain a fast drying.
To find out more about the Green Flash and its formula, discover our article Green Flash: What is more of?
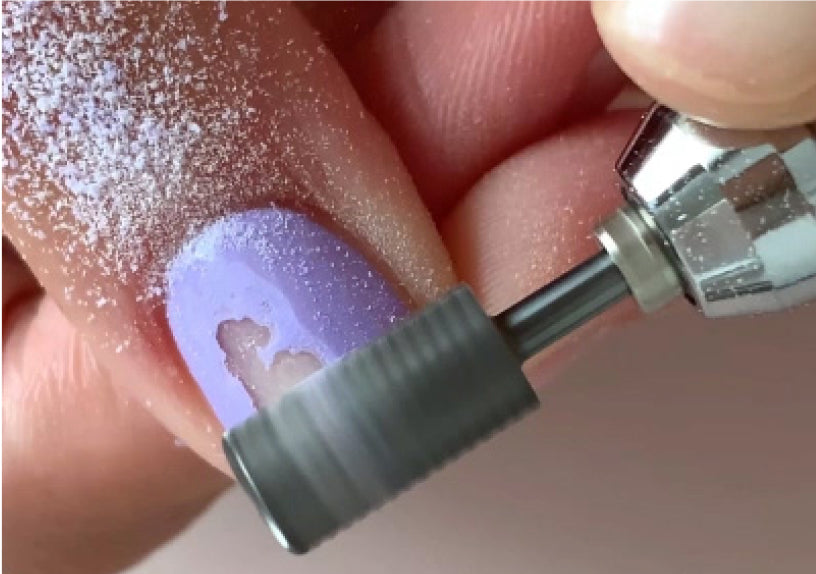
And the dissolving, how does it work?
The principle of solvent is to pass a layer of solid varnish in liquid form to better eliminate it.
In the Polly Green, it is the Succinate diethyl that will allow this varnish liquefaction.
In the Polly Green Flash, solvents are used at the base of the Varnish formula: Butyl Acetate and Ethyl Acetate.


Questions ? Write us in DM on Instagram : The Manucist team will be happy to answer you.